Radiation Therapy (RT)
The principle of Radiation Therapy (RT) is to use high-energy photon beams to destroy the DNA in cancer cells, so that cancer cells no longer proliferate, thereby killing cancer cells and shrinking tumours.
What is RT?
- Radiation Therapy (RT) is one of the major cancer treatment methods. Its principle is to use high-energy photon beams to destroy the DNA in cancer cells, so that cancer cells no longer proliferate, thereby killing cancer cells and shrinking tumours.
- During RT, some normal cells will also be irradiated by radiation while they have a very high self-healing power. On the contrary, cancer cells cannot recover because they are damaged by radiation, and the tumour is controlled or eliminated.
- RT is localized and mostly performed with a Linear Accelerator (Linac) without causing any heat or shock.
- A course of RT is ranged from several to dozens of sessions, and each fraction lasts from a few minutes to more than ten minutes.
- After each session no radiation remains within the animals so the animal owner can assure to live with it afterward.
- RT technology has been adopted on cancer patients for more than 80 years in Hong Kong. Until today, this treatment has developed maturely and reliably.
Applications of RT
1) Curative RT
- RT is the main method of cancer treatment, and its purpose is to completely destroy cancer cells and heal patients.
- It can also be used in combination with chemotherapy or immunotherapy to enhance the therapeutic effect.
- Mainly in combination with surgery, it can be preoperative and postoperative.
- Preoperative and postoperative RT is used to shrink the tu tmouro improve the feasibility of surgery and the chance of complete resection.
- Preoperative and postoperative RT is used to destroy the residual cancer cells, reduces the risk of recurrence and improves overall survival.
- For relieving pain and discomfort caused by tumours, thereby improving the quality of life and controlling symptoms for animals suffering from tumours.
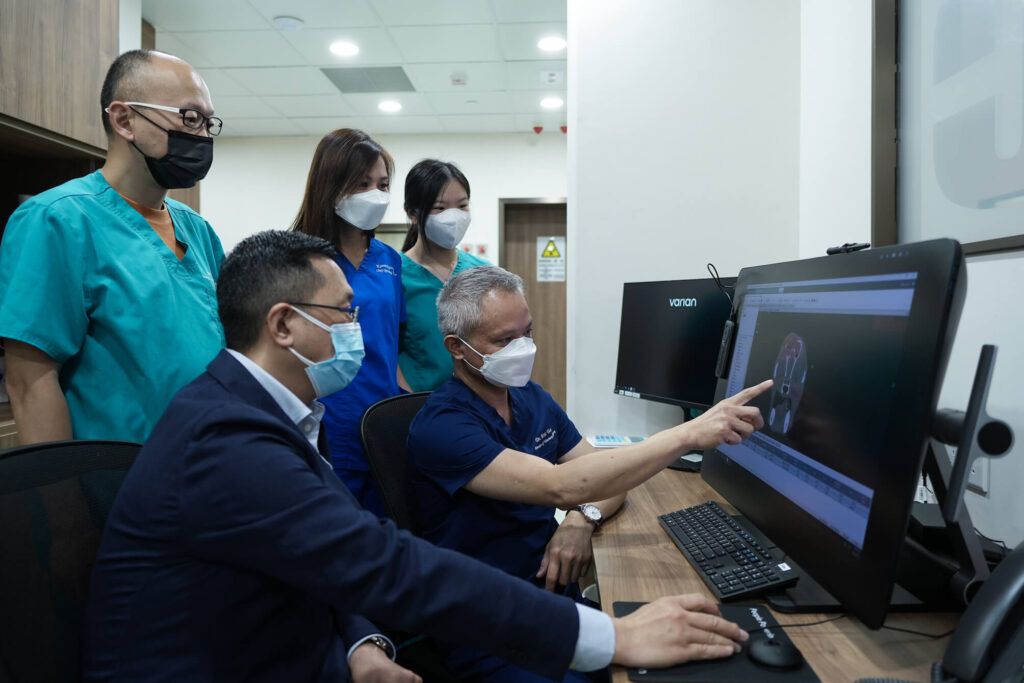

RT Techniques
- When using conventional radiation therapy, an oncologist will contour the three-dimensional shape of irregular tumours and design a treatment plan through 3-Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy (3DCRT) or Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT).
- The course is carried out in multiple sessions and small fractional doses. Each treatment can be completed in a short time. However, due to a large number of sessions, the number and risk of anaesthesia received by the patient have also increased accordingly.
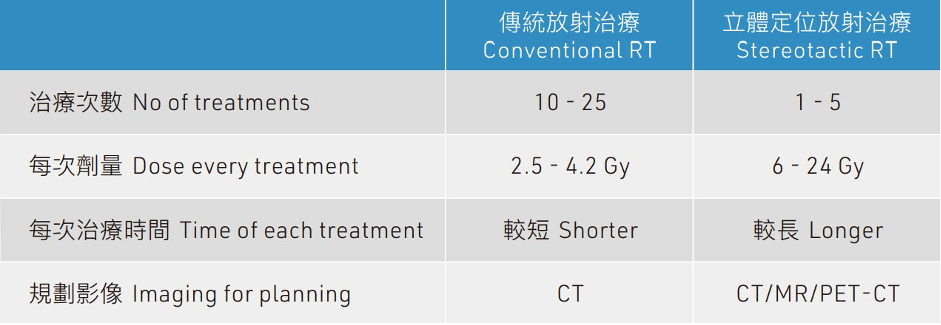
SRT is a state-of-the-art modality involving a high dose per fraction delivered in fewer fractions. With the aid of the treatment planning system and image-guided technique, it delivers a high-precision radiotherapy. Treatment planning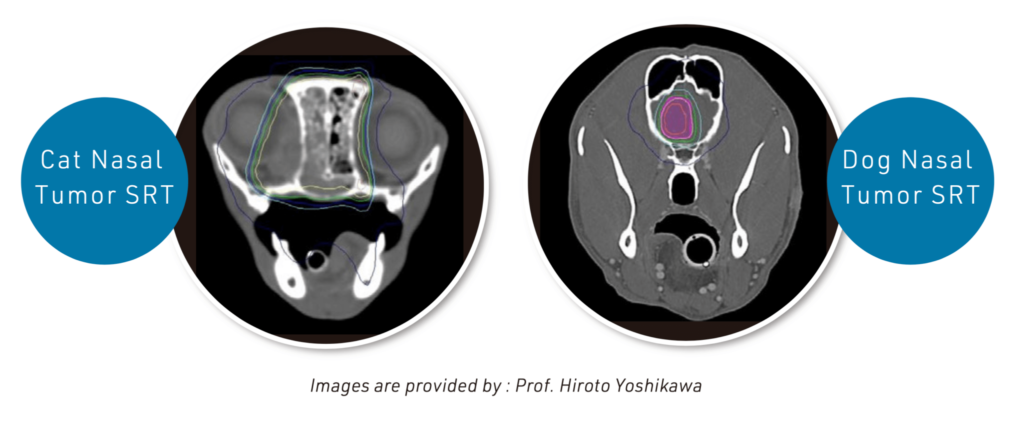
- Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) is an advanced technique that delivers radiation doses to the tumour from different angles. IMRT can trace the changes of tumour location from different angles to improve the conformality of the dose distribution to the different shapes and intensities of the tumour. When tumours are deep in normal tissues or close to organs at risk, IMRT can improve tumours’ radiation dose coverage and reduce toxicity.
- Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) can be regarded as an extension of IMRT. During the treatment, the gantry rotates around the patient and simultaneously delivers radiation dose.
- Combined with medical imaging and radiation therapy technology, it can locate and monitor the tumor location, size and shape before treatment, thereby improving the accuracy of radiation therapy.
- Our centre facilitates Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) built in the linear accelerator to perform positioning and adjustment before each treatment to ensure the accuracy of treatment

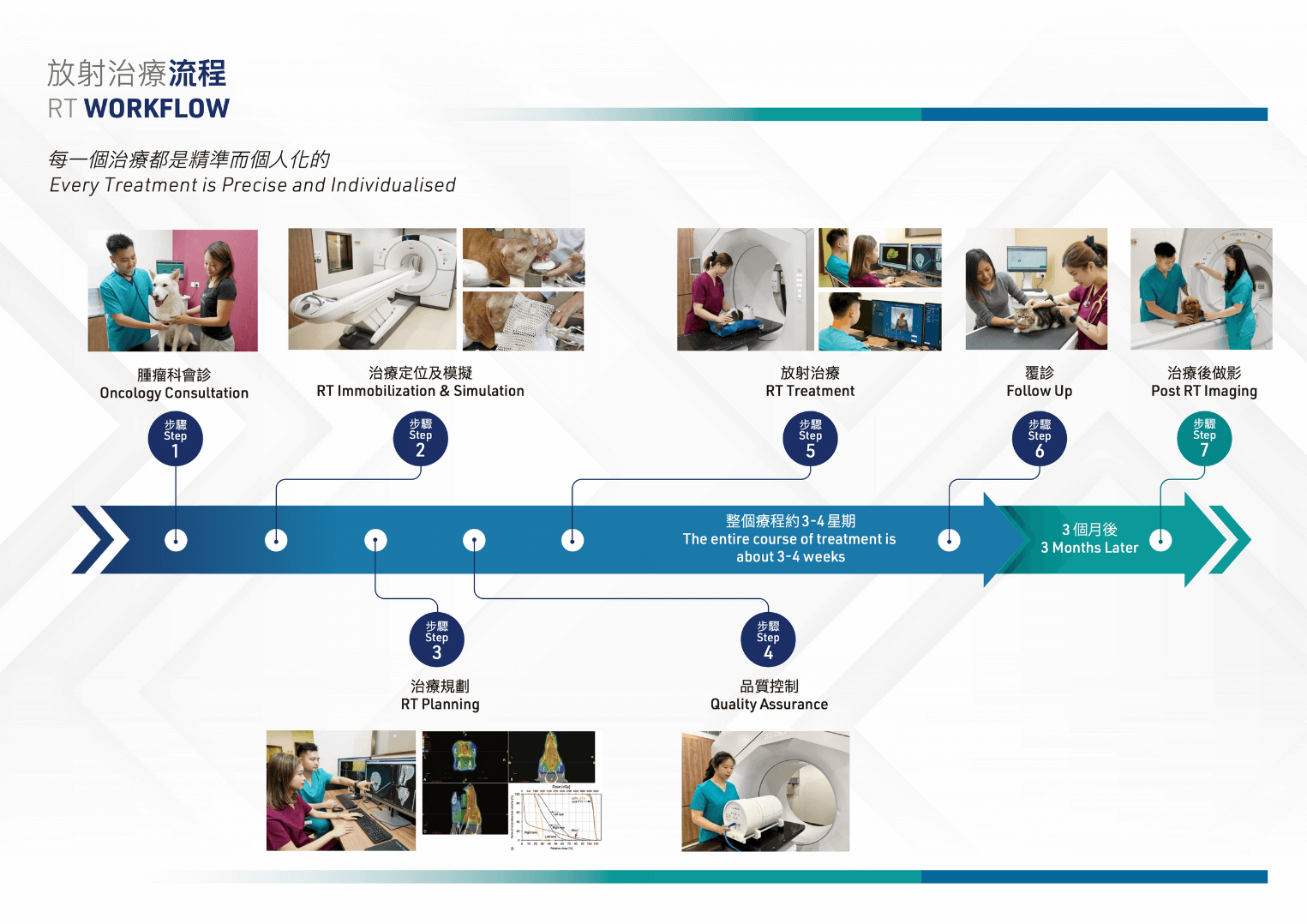
RT Workflow
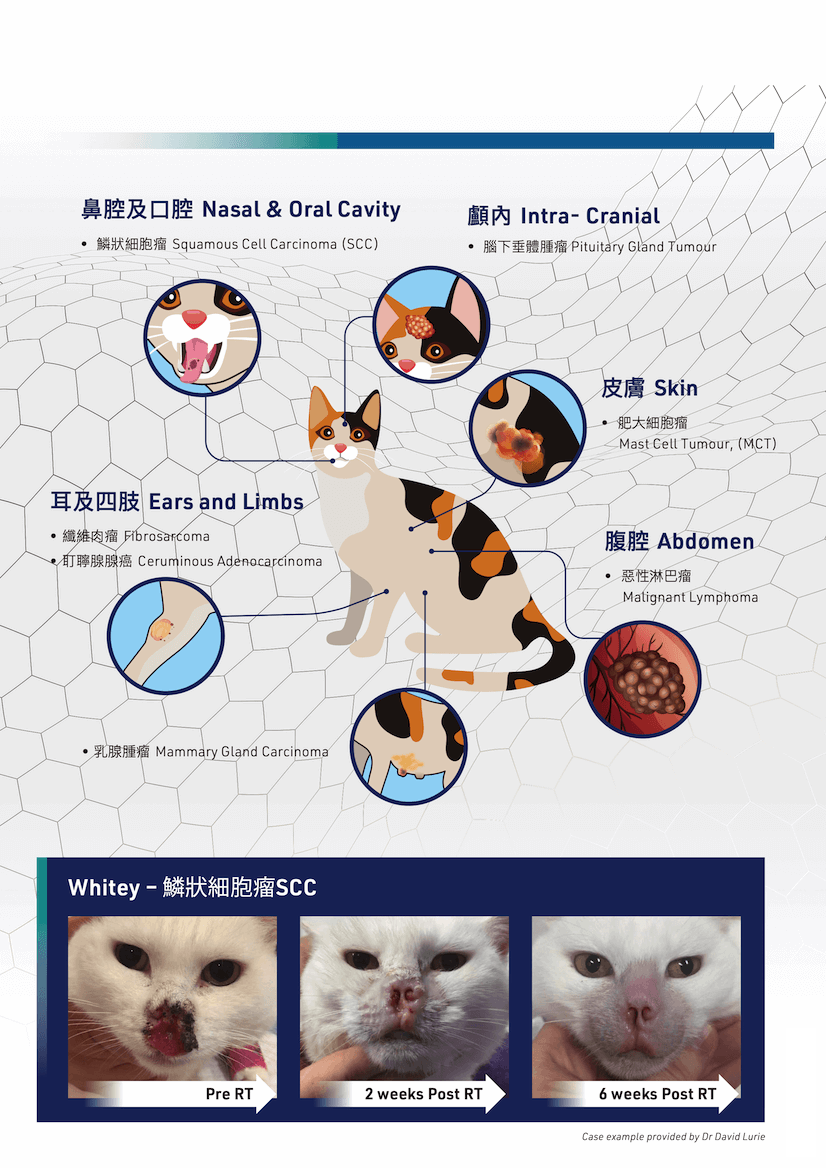
Tumours Suitable for RT and Case Examples

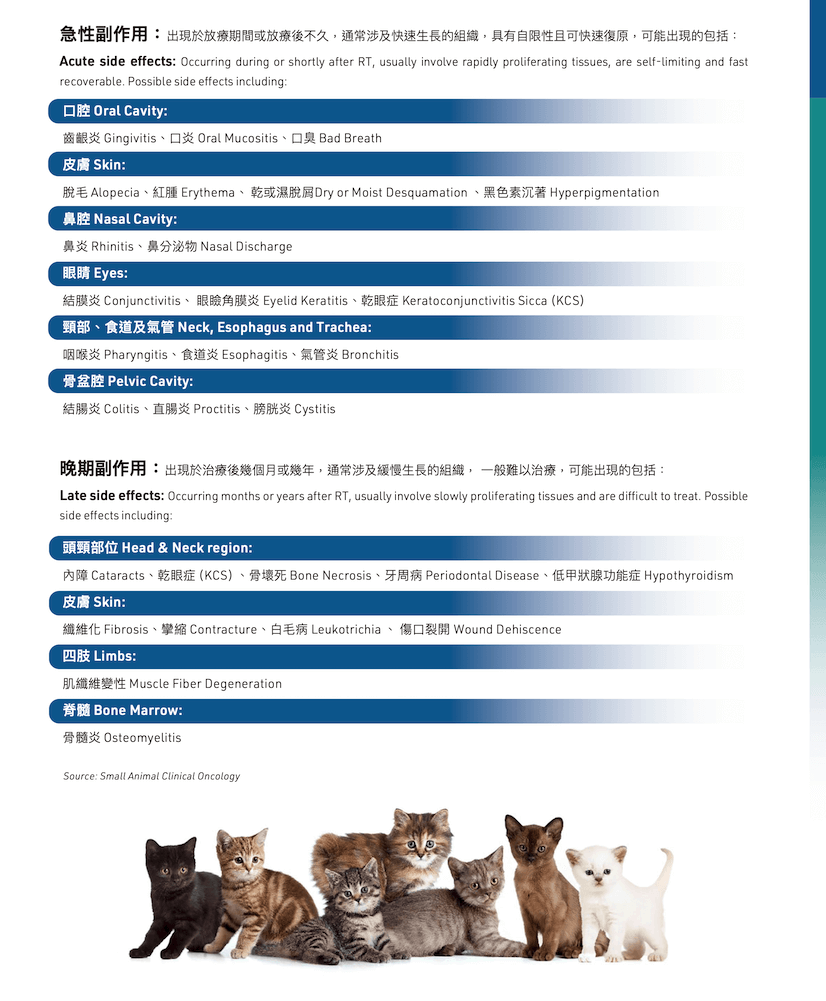
Side Effects